WHY INSULATE? — AN INTRODUCTION TO INSULATION
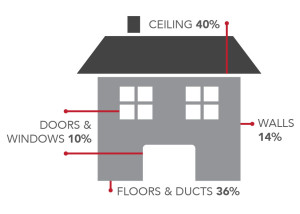
Although insulation is an essential component of a home or building, it is often the least understood. Many people aren’t aware of the multiple places energy is lost in a home. As an Owens CorningTM Certified Energy Expert®, we understand the science behind the building envelope. RCI can help talk you through any questions about insulation that you may have.
Why Insulate?
Insulation lays a foundation of energy efficiency for residential, commercial and industrial structures. It is one of the most cost-effective ways to save energy and reduce monthly utility bills. Whether you are remodeling a home or building a new business, well-installed insulation offers a host of short-term and long-term advantages:
- Increased, more consistent interior comfort all year long
- Reduced energy usage
- Lower heating and cooling costs
- Less wear and tear on HVAC equipment
- Reduced noise transmission for a quieter space
- Improved air quality
- Reduced moisture intrusion
- Less overall environmental impact

How Insulation Works
Heat flows from higher temperature areas to lower temperature areas, creating temperature fluctuation within a space. Insulation wraps your home in a protective blanket, reducing heat flow in order to keep the heat out during warmer months and the heat in during cooler months. Insulation is an excellent noise absorber and helps to reduce sound transmission from both outside and within a home, creating a quieter space with less reverberation. Insulation also allows other energy-efficient components, such as air sealing, to do their job, forming a comprehensive insulating system that helps maintain consistent temperatures and moisture levels, reduce energy usage and increase monthly utility savings.
What Is R-Value?
The “R” in R-value stands for resistance to heat flow. The higher the R-value, the higher the level of resistance and the greater the insulating power. R-value requirements vary depending on climate and building type.
Below is an example of how R-value relates to the amount of insulation used in a typical attic. The thicknesses listed are for Owens Corning PROPINK® L77 Loosefill Insulation blown in the attic and not a general rule of thumb for any other brand/type of insulation in any other areas/applications. RCI can provide you the correct amount of insulation for your project and the R-value you want to achieve.
| R-value | Minimum Thickness (in) |
| R-13 | 4.75 |
| R-19 | 6.75 |
| R-22 | 7.75 |
| R-26 | 9 |
| R-30 | 10.25 |
| R-38 | 12.75 |
| R-44 | 14.75 |
| R-49 | 16.25 |
| R-60 | 19.5 |
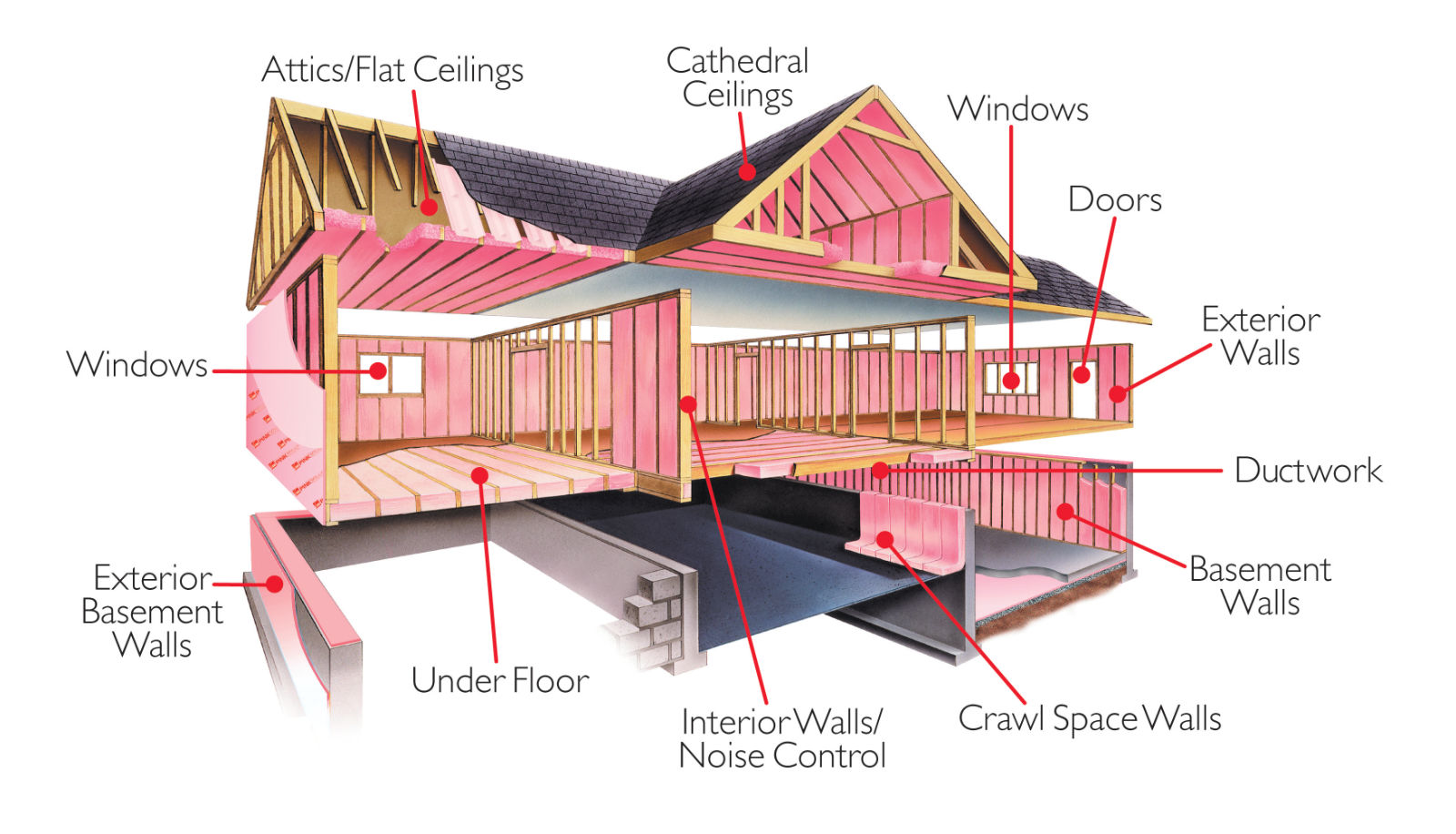
Where to Insulate
Insulation should be installed in walls, floors, attics, basements and crawlspaces. A more detailed list includes:
- Ceilings with unheated spaces above, including dormer ceilings
- Knee walls of attic spaces finished as living areas
- Sloped walls and ceilings of attics finished as living areas
- Cathedral or vaulted ceilings
- Around perimeters of slabs
- Floors above vented crawl spaces
- Floors over unheated or open spaces such as over garages or porches
- Basement walls
- Band and header joists
- Interior walls, ceilings or floors where extra sound control is desired
- Floors over unconditioned basements
Insulation Types & Materials
Insulation is manufactured in a variety of forms and materials to suit a range of efficiency, structural and budgetary needs. Each option brings its own level of durability, versatility, R-value and cost.
Insulation Types
- Batt & Roll
- Loose Fill
- Rigid Foam
- Spray Foam
Insulation Materials We Install
How Much Insulation Is Enough?
The amount of insulation needed varies depending on location, building type and materials.
Click here to view recommended insulation levels for retrofitting existing wood-framed buildings.
Things to Consider When Insulating
- What type of insulation is being used?
- Does the insulation meet or exceed local building codes and national recommended insulation levels?
- How effective is the insulation (thermal performance, acoustical performance)?
- Is the insulation resistant to moisture, fire and settling?
- Is the insulation material safe and sustainable?
- Is the insulation cost effective?
Based on the specifications of your project, RCI can recommend the best solution for you.
Home Energy Auditing
An energy audit is an in-depth assessment of your building envelope conducted by a certified energy rater. According to RESNET, the authority on home energy auditing, home energy audits have three main objectives:
- Figuring out where and how energy is being lost
- Locating inefficient operating systems
- Determining cost-effective ways to enhance home efficiency and comfort
Knowing the energy trouble spots of an existing structure or the potential energy issues of a new structure allows for comprehensive solutions to be designed and implemented for increased efficiency. RCI is very knowledgeable in identifying and correcting insulation and air sealing deficiencies.
Your House as a System
Though insulation is one of the most essential and cost-effective ways to create overall efficiency, there are many factors to take into consideration that also affect your home’s energy efficiency and performance. Insulation and air sealing combined with energy-efficient appliances, windows, doors, lighting and HVAC equipment build a whole-house efficiency system that will prove beneficial throughout the year and for years to come.
